Nutrition plays a key role in your fitness training. To maximize your workouts, it’s important to fuel your body properly at every stage. The best nutrition for fitness training includes a balanced approach that focuses on carbohydrates, proteins, and hydration. Whether you’re looking to build muscle, boost endurance, or recover effectively, the right diet can make all the difference in your performance and results.
Before exercising, consuming healthy carbohydrates will provide the energy you need to push through your workouts. This can include options like whole-grain toast or fruits. After your workout, focus on proteins and healthy carbs to help with recovery and muscle growth, ensuring your body gets what it needs to repair and strengthen. Staying hydrated throughout is equally crucial for optimal performance.
By understanding the core principles of nutrition for your fitness goals, you empower yourself to make better dietary choices that support your active lifestyle. This foundation sets you up for success, whether you exercise casually or aim for peak performance in your sport.
Key Takeaways
- A balanced diet of carbs, proteins, and hydration is essential for fitness training.
- Pre-workout nutrition helps boost energy, while post-workout meals support recovery.
- Understanding nutrition allows you to enhance your performance and achieve your fitness goals.
Fundamentals of Nutrition for Fitness
Nutrition is key to enhancing your fitness training. It fuels your body, aids performance, and helps with recovery. Knowing the basics of macronutrients and micronutrients will help you make better dietary choices.
Understanding Macronutrients
Macronutrients include carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Each plays a vital role in your training.
- Carbohydrates: They are your body’s main energy source. Consuming complex carbs like whole grains, sweet potatoes, and fruits can provide sustained energy for workouts.
- Protein: Important for muscle repair and growth, protein should be a staple in your diet. Sources include chicken, fish, beans, and dairy. Aim for lean proteins that are low in saturated fats.
- Healthy Fats: Necessary for hormone production and overall health, include healthy fats from avocados, nuts, and olive oil. They are vital for long-lasting energy, especially during longer workouts.
The Role of Micronutrients
Micronutrients, which include vitamins and minerals, support many bodily functions, including energy production and immune health.
- Vitamins: Essential vitamins like B vitamins, vitamin D, and antioxidants help convert food into energy. They help your body recover from workouts and fend off illness.
- Minerals: Key minerals such as calcium and iron play roles in bone health and oxygen transport in the blood. Ensure you get enough through fruits, vegetables, nuts, and dairy.
A varied diet rich in fruits and vegetables can help you meet your micronutrient needs.
Balancing a Fitness Diet
A balanced diet is crucial for your fitness routine. Here’s how you can achieve it:
- Portion Control: Use the plate method. Fill half your plate with fruits and vegetables, a quarter with protein, and a quarter with carbohydrates.
- Regular Meals: Eating every 3-4 hours keeps your energy stable. Include snacks like Greek yogurt or nuts to fuel your workouts.
- Hydration: Water is essential. Drink plenty throughout the day, especially before, during, and after exercise.
By focusing on a balanced intake of macronutrients and micronutrients, you can optimize your nutrition for better fitness results.


Pre-Workout Nutrition
Pre-workout nutrition is essential for maximizing your performance and energy during exercise. The right foods and hydration can help you achieve your fitness goals more efficiently. Focus on timing and nutrient choices to fuel your workouts effectively.
Energy Sources and Timing
To optimize your energy levels, consider the timing of your meals. Eating a balanced meal 1-2 hours before exercise can support glycogen levels. Glycogen is the stored form of carbohydrates in your muscles and liver, which provides energy during workouts.
Key Points:
- Aim for a mix of carbohydrates and protein.
- Carbohydrates provide quick fuel, while protein helps with muscle repair.
Choosing the right energy sources can greatly impact your performance. Consult a nutrition guide to find the best foods for your specific workout plan.
Hydration Strategies
Staying hydrated is crucial for peak performance. Dehydration can lead to fatigue, decreased strength, and poor focus. Before exercising, drink water to ensure your body is ready.
Hydration Tips:
- Consume about 16-20 ounces of water 2-3 hours before working out.
- Drink an additional 8 ounces right before your workout.
If you exercise for more than an hour, consider drinks that contain electrolytes. These can help maintain hydration and replace lost nutrients during longer sessions.
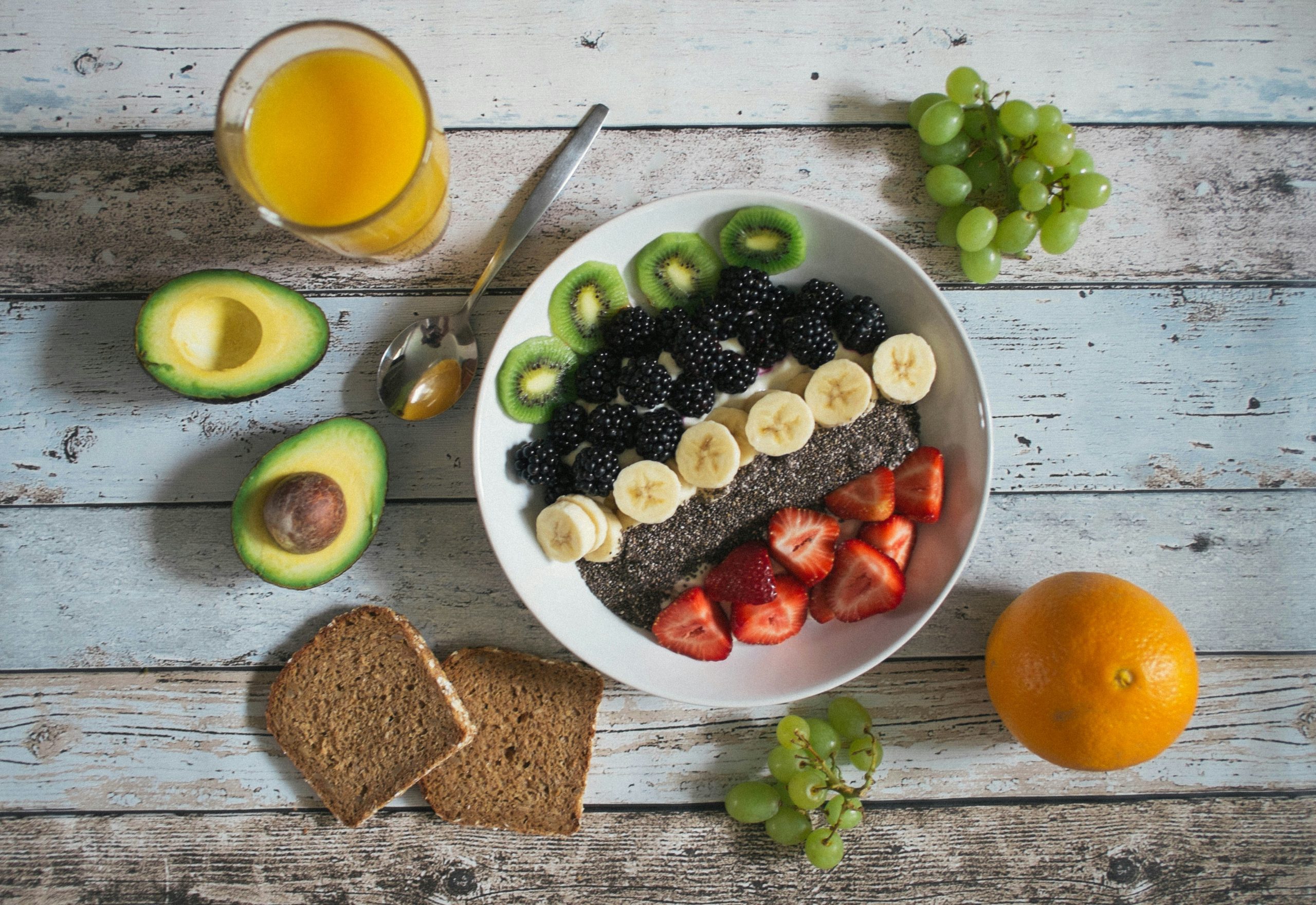
Best Foods for Pre-Exercise
The foods you choose can make a significant difference in your workout results. Focus on nutritious options.
Ideal Pre-Workout Foods:
- Oatmeal with banana and a sprinkle of nuts
- Greek yogurt with mixed berries
- Whole-grain toast with nut butter
These foods provide a combination of carbohydrates for energy and protein for muscle support. Eating these 1-2 hours before your workout can prepare your body for intense exercise.


Nutrition for Muscle Gain and Recovery
To effectively support muscle gain and recovery, it’s important to focus on protein intake, the right recovery foods, and essential amino acids. Each of these plays a critical role in helping you build strength and repair muscle after workouts.
Optimizing Protein Intake
Protein is crucial for muscle growth. Aim for 1.2 to 2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight daily, depending on your activity level. Quality protein sources include:
- Eggs: High in protein and contain all essential amino acids.
- Chicken: Lean meat that offers a great protein punch.
- Greek yogurt: Packed with protein and ideal for post-workout recovery.
Be sure to include protein in every meal and snack. This helps maintain muscle protein synthesis while reducing muscle breakdown. Consuming protein soon after workouts can enhance your recovery process. Try to include sources rich in leucine, an amino acid that stimulates muscle repair and growth.
Recovery Foods and Nutrients
Post-workout nutrition is important for recovery. After exercising, your body needs to replenish energy stores and repair tissues. Focus on a combination of:
- Carbohydrates: Restore glycogen levels. Good options include whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
- Healthy fats: Support overall health. Foods like avocados and nuts can help reduce inflammation.
Sample post-workout meals include:
- Grilled chicken with sweet potatoes
- Salmon with quinoa and spinach
- Tuna salad with whole-grain bread
These meals not only provide protein and carbs but also other nutrients that aid in recovery.
Amino Acids and Muscle Repair
Amino acids are the building blocks of muscle repair. When you consume protein, your body breaks it down into amino acids, which then help repair damaged tissues after resistance training. Key amino acids include:
- Leucine: Promotes muscle growth and repair.
- Glutamine: Supports recovery and immune function.
- Branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs): Reduce muscle soreness and fatigue.
Incorporate foods high in these amino acids, like chicken, fish, dairy, and legumes, to maximize your recovery. Consider a protein shake if you struggle to get enough from food alone. This can be especially beneficial after intense workouts.
Eating for Endurance and Athletic Performance
Nutrition plays a key role in your ability to perform well during endurance activities. Focusing on the right foods can help you maintain energy, stay hydrated, and enhance your performance.
Sustained Energy for Endurance
Carbohydrates are vital for endurance athletes. They are your main source of energy during prolonged exercise. It is recommended that you consume 30-60 grams of carbohydrates per hour of activity. Choose fast-absorbing options like sports drinks, gels, and chews. These will help fuel your workouts without heavy digestion.
In the days leading up to an event, prioritize healthy carbs. Whole grains, fruits, and vegetables will help fill your glycogen stores. This stored energy is essential for supporting your performance during long workouts or races.
Hydration and Electrolytes
Staying hydrated is crucial for maintaining performance. Dehydration can lead to fatigue and poor results. Drink plenty of water in the days leading up to and during your activity. Aim to drink about 500 to 600 ml (17 to 20 ounces) of water two to three hours before exercising.
Electrolytes, such as sodium and potassium, are also important, especially during long events. These help regulate body fluids. Consuming sports drinks or electrolyte supplements during extended exercise can maintain your electrolyte balance. This prevents muscle cramps and supports endurance.
Boosting Performance with Nutrition
After training, focus on recovery to help your body rebuild. Consume 1 to 1.2 grams of carbohydrates per kilogram of body weight within the first few hours after exercise. Adding 0.3 grams of protein per kilogram will support muscle repair.
Examples of good post-workout options include a smoothie made with fruit and yogurt or a sandwich with lean protein. This combination will maximize recovery and prepare you for your next workout. Remember, what you eat can directly impact your endurance exercise and overall athletic performance.
Post-Workout Nutrition and Recovery
After exercise, your body needs proper nutrition to recover effectively and support muscle repair. Focus on what you eat and drink right after your workout to enhance recovery and prepare for your next training session.
The Importance of Post-Exercise Meals
Eating after a workout is crucial for recovery. Your body has just expended energy and broken down muscle tissue. Combating muscle fatigue is essential for progress. The best time to eat is within 30 to 45 minutes post-exercise.
Aim for a meal that includes proteins and carbohydrates. Protein aids in muscle repair and carbohydrates replenish your energy stores. A simple choice could be a grilled chicken sandwich or a protein shake with fruit.
Nutrition and Muscle Recovery
Proper nutrition supports muscle recovery in several ways. After your workout, your muscles need protein to initiate protein synthesis. This process helps repair and build new muscle fibers.
Incorporating antioxidants found in fruits and vegetables can minimize oxidative stress caused by intense exercise. Consider foods like berries, spinach, and nuts for added benefits. Aim for a meal with a 1:1 or 1:2 protein-to-carb ratio for optimal recovery.
Replenishing Glycogen and Nutrients
Your body’s glycogen stores are essential for maintaining energy levels. After exercise, focus on replenishing these stores with carbohydrates. Foods like rice, pasta, or sweet potatoes can effectively restore glycogen.
Additionally, hydration is key. Drink water or electrolyte beverages to replace fluids lost during workouts. Pair your carbohydrates with protein to maximize recovery and enhance muscle healing. Consider a snack like a banana with almond butter for a balanced approach to recovery.